 Jamming is a form of electronic attack which uses a stronger signal to disrupt target wireless devices.
DISCLAIMER: It is an offence to intentionally interfere with someone else’s use of the wireless spectrum in the UK.
The mention of its name also disrupts rational thinking amongst otherwise intelligent people and its common for spectrum planners and event managers to ignore signal theory when discussing its impact and revert to hollywood instead.
Originally used in warfare, it’s now commonly used in civil emergencies such as event protection, bomb disposal or hostage negotiation.
This blog uses modelling evidence to demonstrate the impact of jamming in a city and in the process, debunk popular jamming myths. The target band in all models is the 2.4GHz ISM band which is easily the busiest unlicensed band in the world and home to WiFi, Bluetooth, CCTV, Locks, Sensors, Drones and phones. The chosen location is George Square in Glasgow which is a large open surrounded by tall stone buildings. The antenna used is Omni-directional to visualise the effect in all directions.
Jamming is a form of electronic attack which uses a stronger signal to disrupt target wireless devices.
DISCLAIMER: It is an offence to intentionally interfere with someone else’s use of the wireless spectrum in the UK.
The mention of its name also disrupts rational thinking amongst otherwise intelligent people and its common for spectrum planners and event managers to ignore signal theory when discussing its impact and revert to hollywood instead.
Originally used in warfare, it’s now commonly used in civil emergencies such as event protection, bomb disposal or hostage negotiation.
This blog uses modelling evidence to demonstrate the impact of jamming in a city and in the process, debunk popular jamming myths. The target band in all models is the 2.4GHz ISM band which is easily the busiest unlicensed band in the world and home to WiFi, Bluetooth, CCTV, Locks, Sensors, Drones and phones. The chosen location is George Square in Glasgow which is a large open surrounded by tall stone buildings. The antenna used is Omni-directional to visualise the effect in all directions.
Jamming thresholds
IEEE standard protocols such as 802.11 have defined thresholds for Energy Detection (ED) above which they will not transmit. If you can hit this threshold then devices will refuse to transmit and can be considered ‘jammed’. For 802.11 the energy detection threshold is -62dBm which is a strong wireless signal. You would need to be in the same room as the wireless router to see a signal this strong so to be effective you must be close or just be very very powerful like a military airborne jammer.Power limits
In Europe the power limit for 2.4GHz is 0.1 Watt or 20dBm which is what a domestic Wi-Fi router radiates. This is low by design to minimise interference, conserve battery and enhance privacy against eavesdropping. In the US it’s higher at a generous 1 Watt / 30dBm which still works since everyone is even when competing for channel access, just on a bigger scale. Jamming someone within this limit is hard. You either need to get very close (~10m) or use a directional antenna. For jamming of a wide area like the whole square and beyond you would need hundreds of watts of power. You can deliver this efficiently with a directional antenna and reduce collateral damage in the process but jamming a wide area with a ground based jammer requires an enormous amount of power. Siting the jammer above the clutter is much more efficient.Simulating jamming
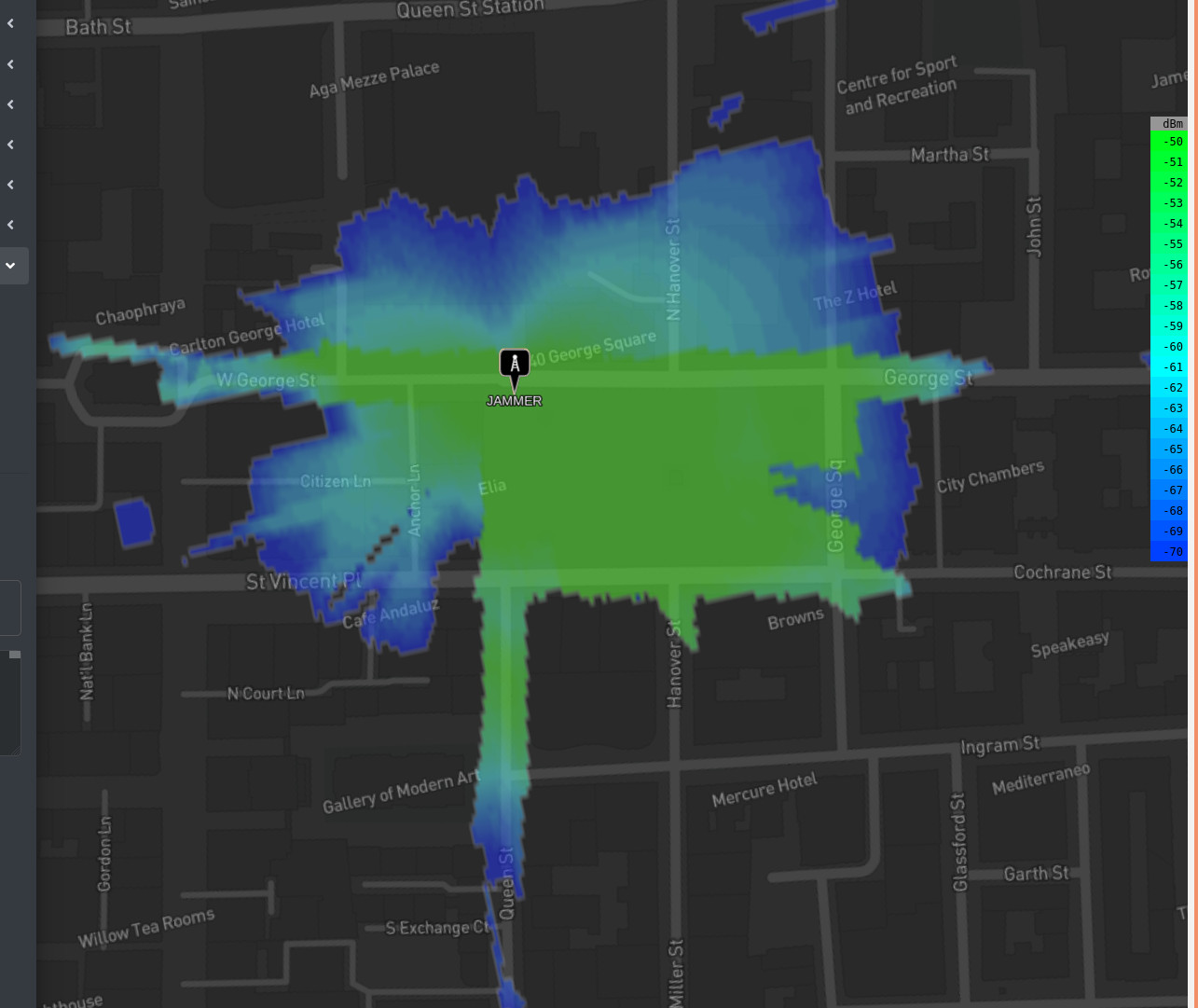
The key setting for simulating the effect of jamming is the receiver threshold. Creating a radio coverage map with a ‘normal’ threshold like -90dBm would not be useful unless you were intent on producing a misleading result to support an argument against using jamming. For an accurate map of jamming ‘effect’ you need to see the coverage at the ED threshold (-62dBm). Within the web interface this is under the ‘Receiver’ menu and in the api it is the ‘rxs’ parameter.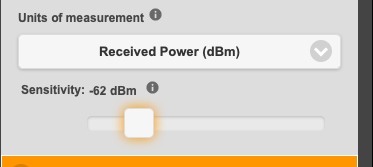
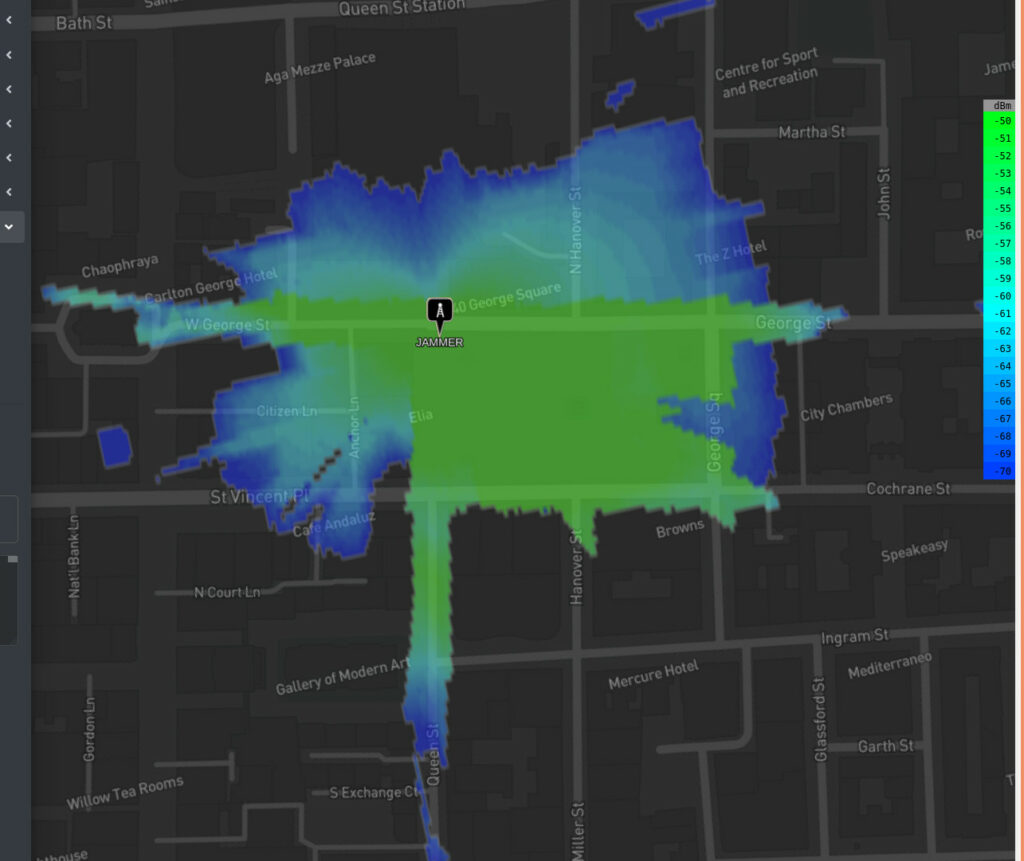
10 Watts
Using a 2.4GHz frequency and an omni-directional antenna the protection “bubble” covers the square at ~200m radius but not much else due to building attenuation. A value of 3.0 dB/m was used the neighbouring stone buildings.
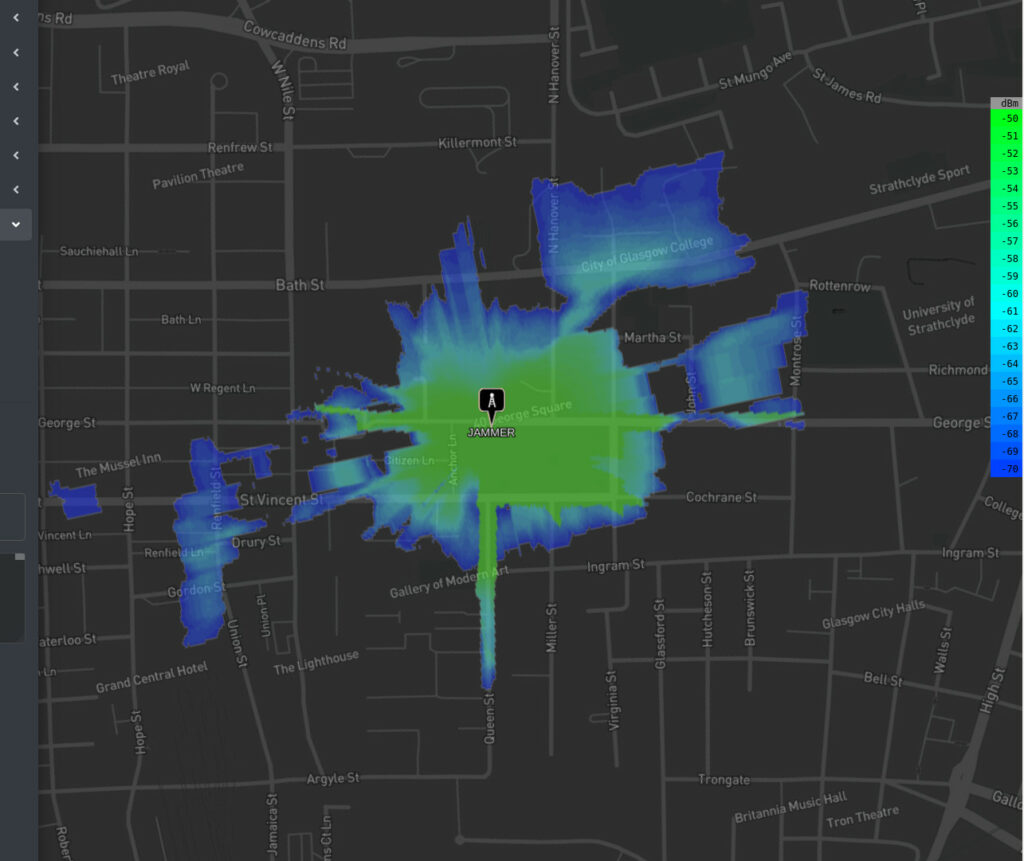
100 Watts…
Increasing the power by a factor of 10 does little to the bubble due to the way power decays logarithmically. The stone buildings are still blocking the signal so the bubble extends out to ~400m now with a gain toward a piece of high ground to the north east and down straight streets where there’s line of sight.
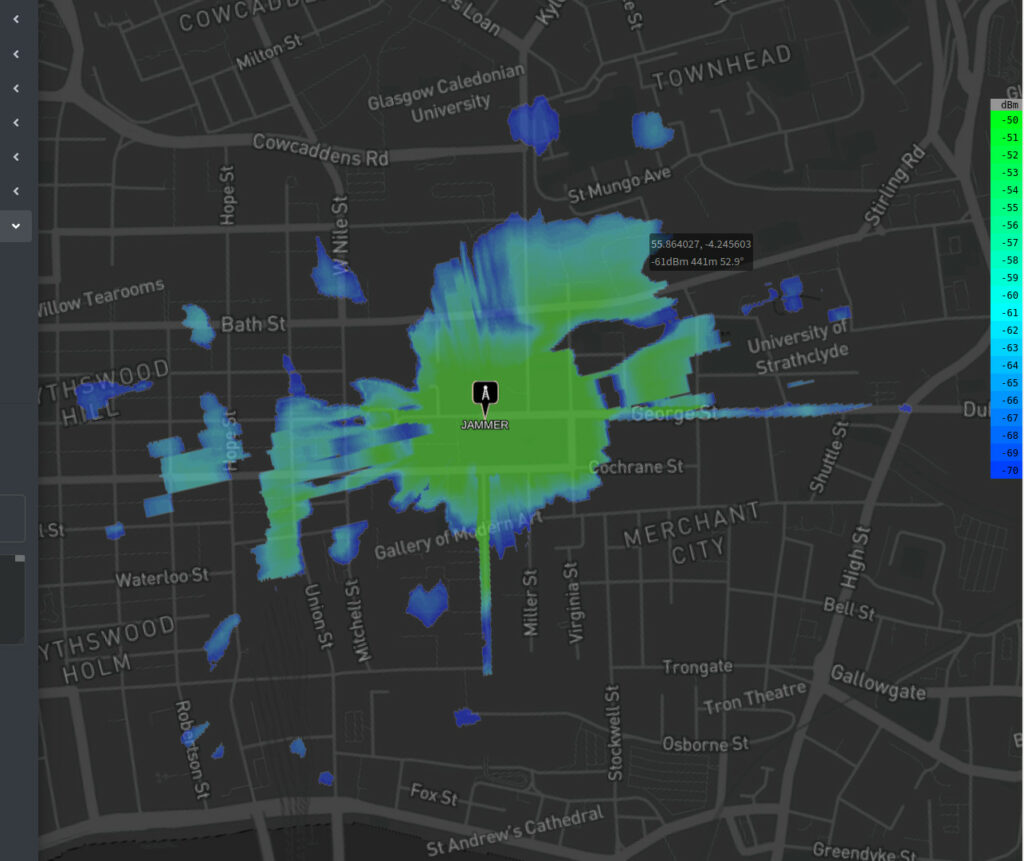
1000 Watts?…
If you were higher than the buildings, 1KW would jam devices at 7km according to the Friis path loss model. Down on the street however it’s a different story and the bubble is extending only a few hundred metres beyond the square and further down streets with line of sight.
Summary
Antenna siting, not RF power is how to get the best out of a jammer and urban modelling is essential for maximum effect and to minimise collateral damage, especially in the ISM and cellular bands.
People won’t die, but they will get confused
The greatest fear with collateral damage is disruption to ISM medical devices such as wireless implants. If you jammed inside a hospital where ISM band equipment is used, you could disrupt medical equipment but to influence it from beyond the hospital walls would require several kilowatts of RF delivered very nearby to penetrate the walls with enough power to still exceed the ED level. Wireless medical devices are designed for failure. They are after all used in the busiest spectrum in the busiest cities in the world and have back-off and interference coping mechanisms built in to the standard, like 802.11’s -62dBm ED level and random back-off timer to manage channel contention.
Vehicles won’t crash, but they might stop playing music
The 2.4GHz band is a healthy distance from 1.5GHz where GPS resides. Jamming one to target data communications does not influence the other unless your equipment is really poor. Even if you did interfere with vehicles navigation systems, they are distinct, again by design, from control systems since the spectrum is shared and prone to interference. The most likely impact would be on Bluetooth which uses the entire 2.4GHz band and is commonly used in vehicle infotainment systems which would suffer interference.