Web Interface Map
Managing Layers
Any created heatmap Layer(s) will be displayed on the map and listed as a filename with a checkbox in the top right corner.
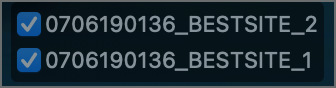
You may enable or disable the layers as per your requirement by simply checking and unchecking the checkboxes.
To clear the layers from the map (but not delete them from your archive) use the recycle button on the top menu.
To hide the list of layers if it becomes very long, use the layer list toggle button located next to the search and home icon. Click it once to hide the list and again to show the list.

My Obstacles
Custom obstacles or Clutter can be defined as anything which could impede a signal’s path.
For RF planning purposes, the clutter can predominantly be trees and buildings. As the trees and the buildings vary greatly in density, you may wish to, we have included their different types.
The global clutter data for telecommunications planning is very expensive, and often outdated, despite their price. We have developed a much more flexible way of self-generating accurate clutter models.
Whether you need to define one big building which is being planned for construction or you need to upload a plan for an entire city - we support both DIY (Do It Yourself) and BYO (Bring Your Own) clutter.
DIY Clutter - You can draw your own clutter directly in the Cloud-RF interface to meet your requirements, defining the Type of the clutter.
BYO Clutter - You can upload your own KML / GeoJSON file directly.
DIY Clutter
DIY clutter allows you to draw and build your clutter directly in the Cloud-RF interface to meet your requirements.
Click on the Draw obstacles button
 icon to draw custom clutter located at the bottom-left of the interface.
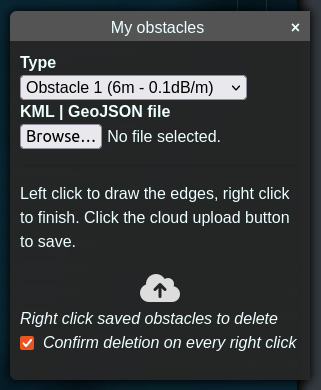
icon to draw custom clutter located at the bottom-left of the interface.The My obstacles Dialog box will appear.
For information regarding Drawing Clutter, refer to the Drawing a Polygon section.
The dialog box is split into several parts.
Type determines the type of the material under which you clutter will be allocated. This is for DIY clutter. The value set here will be taken based upon your clutter profile which you select in the “Environment” menu from the “Profile” dropdown on the input menu on the left of the interface. This is used to determine the height, attenuation, name and colour of the clutter.
The “Browse”/”File” button is used to submit KML or GeoJSON files for BYO clutter.
The upload button is used to send your clutter to the Cloud-RF service to handle your clutter.

The checkbox at the bottom for “Confirm deletion on every right click” is a safety catch as you may have multiple clutter on your profile - rather than having to confirm deletion of every one you might decide to disable this checkbox at which point right-clicking on a clutter will instantly delete it without any confirmation.
Drawing Custom Clutter
To define a clutter polygon:
Click on the Draw Obstacles
 icon located at the bottom-left of the interface.
icon located at the bottom-left of the interface.Left-Click on the map to draw the edges of the polygon as per your requirement.
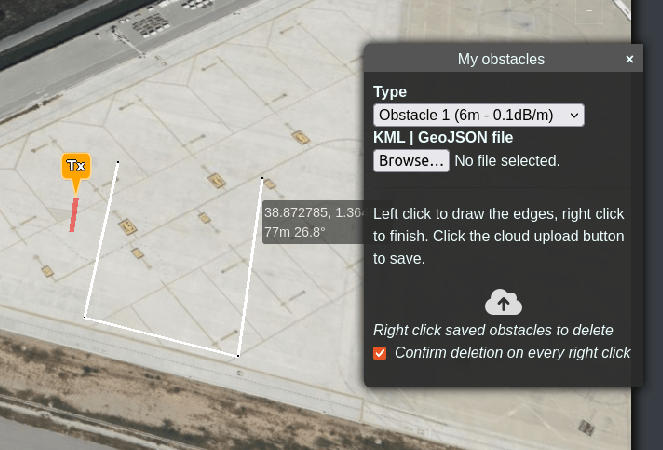
Right-Click to finish. You can repeat as many times as necessary to draw multiple polygons with the same properties.
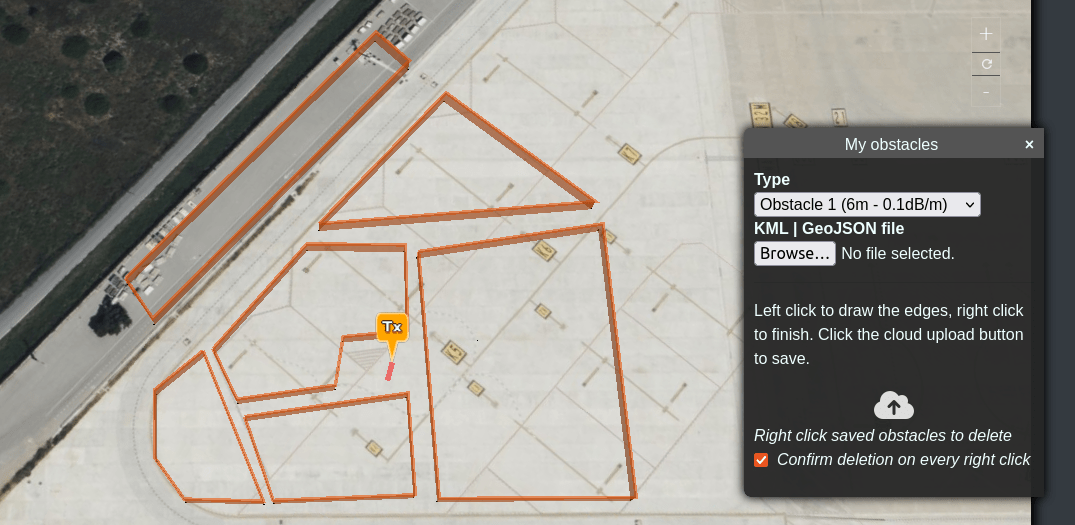
You can change the “Type” to draw as many different types of clutter as you wish with the available types you have to work with. The properties of each type is taken from your clutter profile.
The Custom Clutter Dialog box will also be displayed.
For more information, refer to the Custom Clutter section.
After you have finished drawing your clutter you should then click on the upload button.

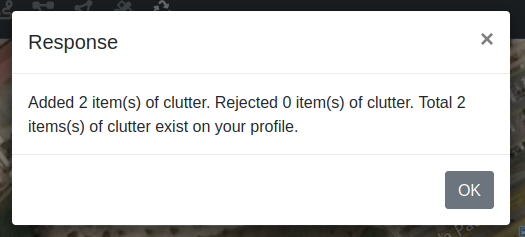
You will be presented with an overview of the clutter which was uploaded to your profile.
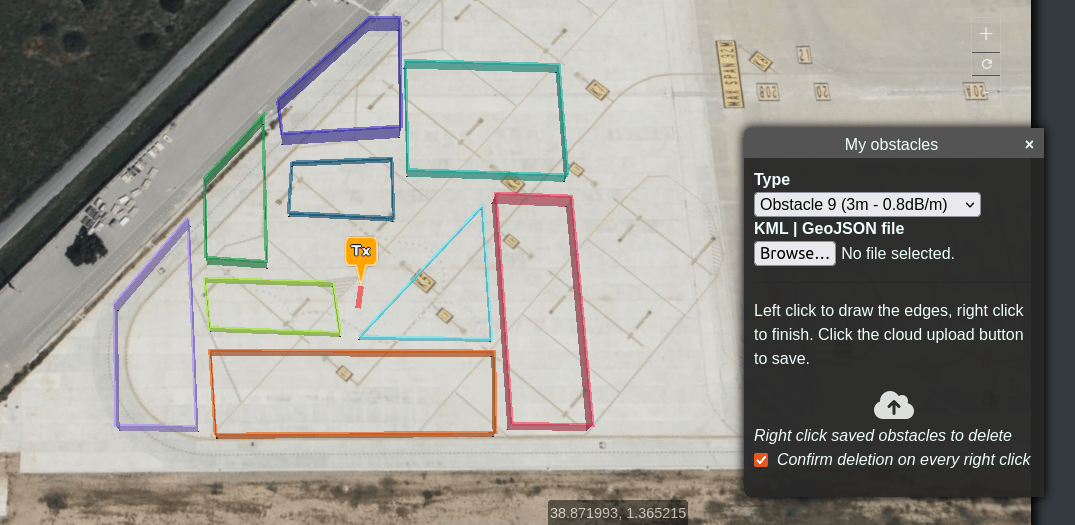
When you close the clutter menu your drawn clutter will be displayed on the map. You can left-click on it to show its properties.
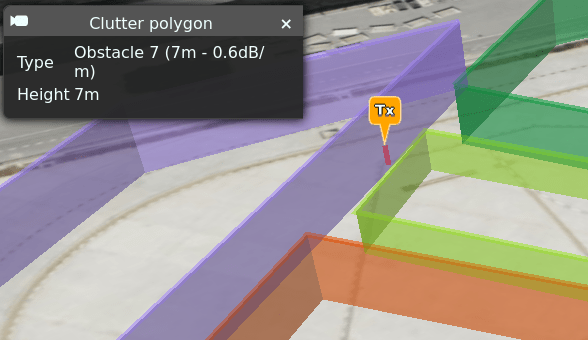
Selecting/Changing Clutter Type and Height
Clutter properties are applied based on the Type you choose from the clutter dialog box.
The attenuation and height for these types are defined in your clutter profile which is selected from the “Environment” menu.

You can choose different clutter profiles to match your environment, or you can create your own clutter profile to define your height and attenuation by clicking on the “Clutter Manager” button. 
From the clutter profile manager you can create and define your own attenuation and heights for listed materials.
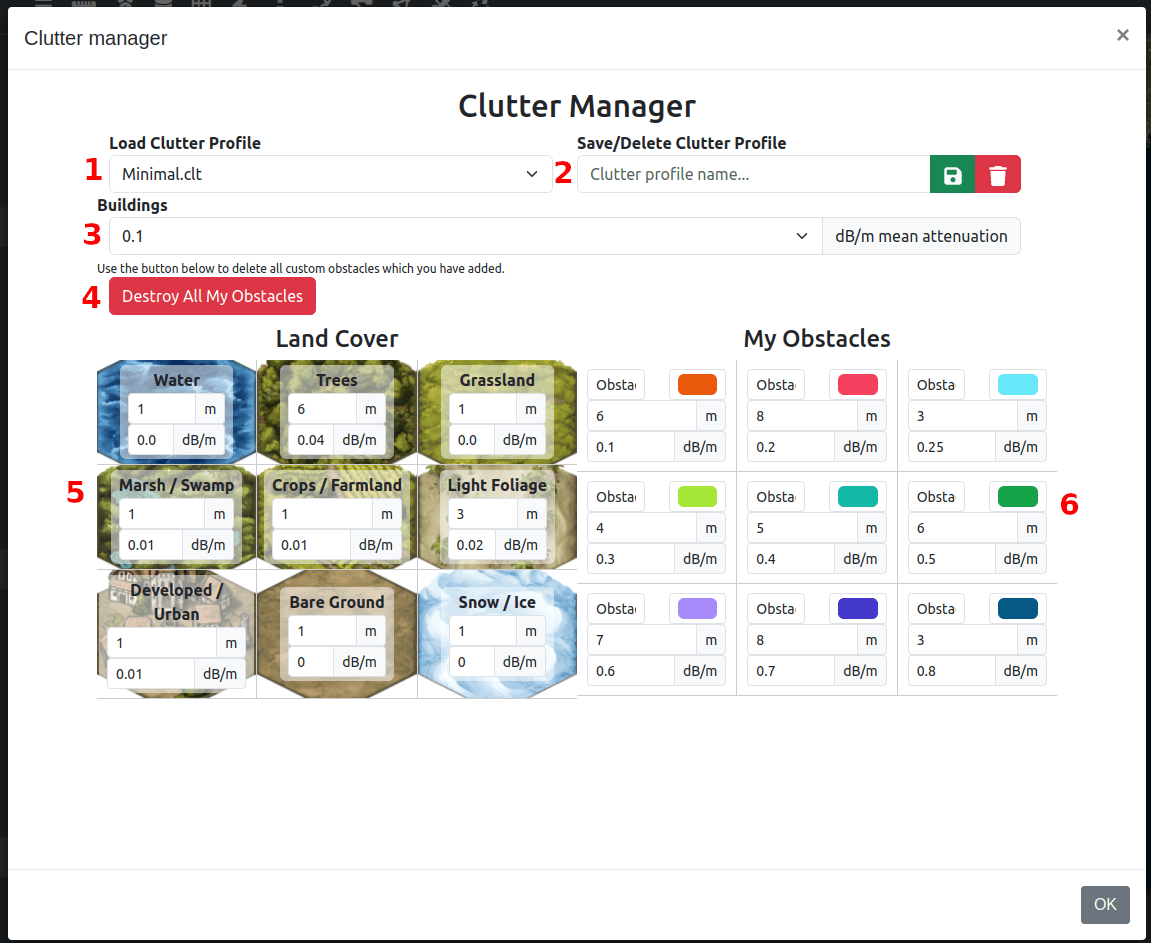
Selected clutter profile
Save/delete profile as name
Building attenuation
Delete all obstacles on your account
Land cover types with customisable height and attenuation values
My obstacle (clutter) types with customisable name, colour, height and attenuation values
Deleting Clutter Profile
If you wish to delete a custom clutter profile then please enter its name into the input box then press on the delete button. Please note that the name must exactly match, including the casing and the extension name. You are also unable to remove system clutter profiles.
BYO Clutter
Uploading a KML / GeoJSON file
This is a BYO type of clutter.
You can import multiple clutter items as a KML or GeoJSON file.
Open the custom clutter menu by selecting the Draw obstacles button
 icon located at the bottom-left of the interface.
icon located at the bottom-left of the interface.Click on Choose File button.
Select the desired KML/GeoJSON file.
Click on the Upload
 icon to save the clutter.
icon to save the clutter.A Response box will be displayed stating that the Clutter has been added.

Viewing the Defined Clutter
After drawing, defining and uploading the clutter, you can view the defined clutter on the map.
Polygon Clutter

Deleting Clutter
To delete a clutter:
Right-Click on the respective clutter on the map.
If you had the “Confirm deletion on every right click” checked in the custom clutter dialog box then you will be prompted to confirm deletion of each peice of clutter. Otherwise the clutter will be deleted without any confirmation.
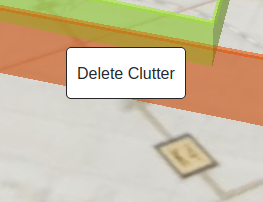
You can also delete all clutter in your profile by opening the clutter manager and pressing the “Delete my obstacles” button.
LiDAR
LiDAR data is the highest accuracy data available and is available for many cities at 2m resolution.
Check the coverage map to see if you are covered.
It’s a surface raster, hence, it is not permeable like the custom clutter but is very useful for line of sight analysis as even trees and bushes are represented.

Mobile View
Touch Screen Gestures
You can pan view, zoom, tilt and rotate on your touch screen phone using the following finger gestures:
Pan Map
You can pan the map by selecting with a single finger and dragging your finger across the screen.

Zoom Map
You can zoon the map by placing two fingers on the map and pinching the fingers together or away from one another to either zoom in or zoom out, respectively.

Tilt Map
You can tilt the map by placing two fingers on the map and dragging them both in the same direction up or down the screen.

Rotate Map
You can rotate the map by placing two fingers on the map and rotating your hand clockwise or counter-clockwise.

Outputs
Embed Code
The new Embed Code functionality lets you Copy the HTML code and upload it to your website with the desired filename and the html extension.
You can reap the following benefits and more using the HTML Embed Code functionality:
Build your own Coverage Map.
Create radio heatmap for your website.
Add Google Maps to your website.
Add RF Coverage on the Google Maps.
For more information regarding this, refer to the Embed Code Benefits topic.
To access the Embed Code functionality:
Click on My Archive
 button on the Function Menu.
button on the Function Menu.The My Archive dialog box will appear.
Click on the HTML Embed Code
 icon.
icon.The Embed Code dialog box will appear.
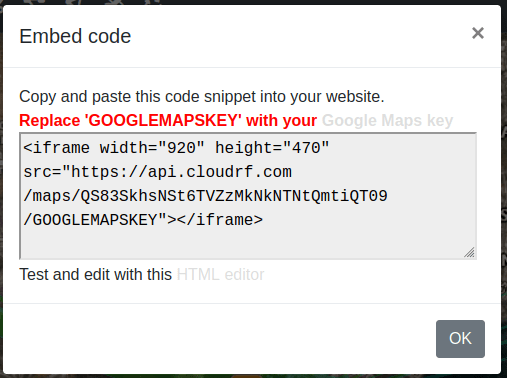
You can copy the HTML code snippet from here and paste it to your website.
Replace the
GOOGLEMAPSKEYin the code with your Google Maps Key.You may Test and Edit the code snippet with the help of HTML editor
Build Your Own Coverage Map
Are you a wireless internet service provider or an organisation that requires an online coverage map to be displayed on their website?
Building your own Coverage Map is just a few clicks away…
The most basic option is to accomplish this is using an arbitrary polygon on a free map like Google Maps. However, if you require a beautiful and accurate physics-based coverage map, at no extra cost, CloudRF’s Embed Code functionality is all you need.
Using the CloudRF’s Embed Code functionality is the easiest way to add a map to your website or blog that supports the HTML content. You just need to copy-paste an HTML code snippet to your website and replace the GOOGLEMAPSKEY in the code with your own Google Maps API key.
For further information regarding Hosting your own Network Map, click on this link.
Create Radio Heatmap for Website
The Embed Code functionality lets you create the radio heatmap for your website.
With the help of GIS mapping and the LIDAR Imaging from the satellites, the CloudRF tool will output a heatmap of the signal strength on the 3D map. Hence, you can create the radio heatmap for your website and also determine how well your signal propagate based on some variables that you configure in the tool.
For further information, refer to this link.
Add Google Maps to the Website
All you need is a web browser and you are just three steps away from adding the Google Map plus RF layer to your website:





 Address search
Address search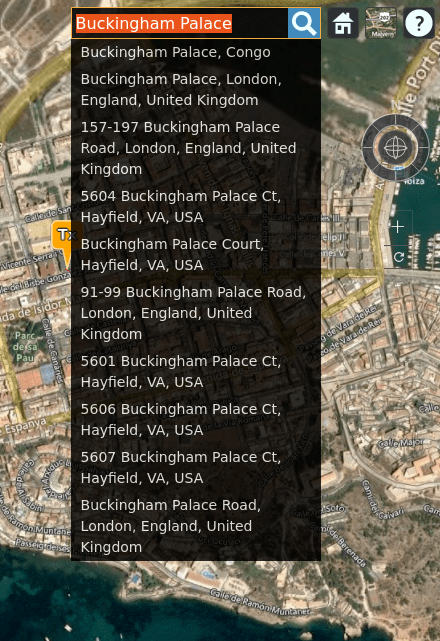
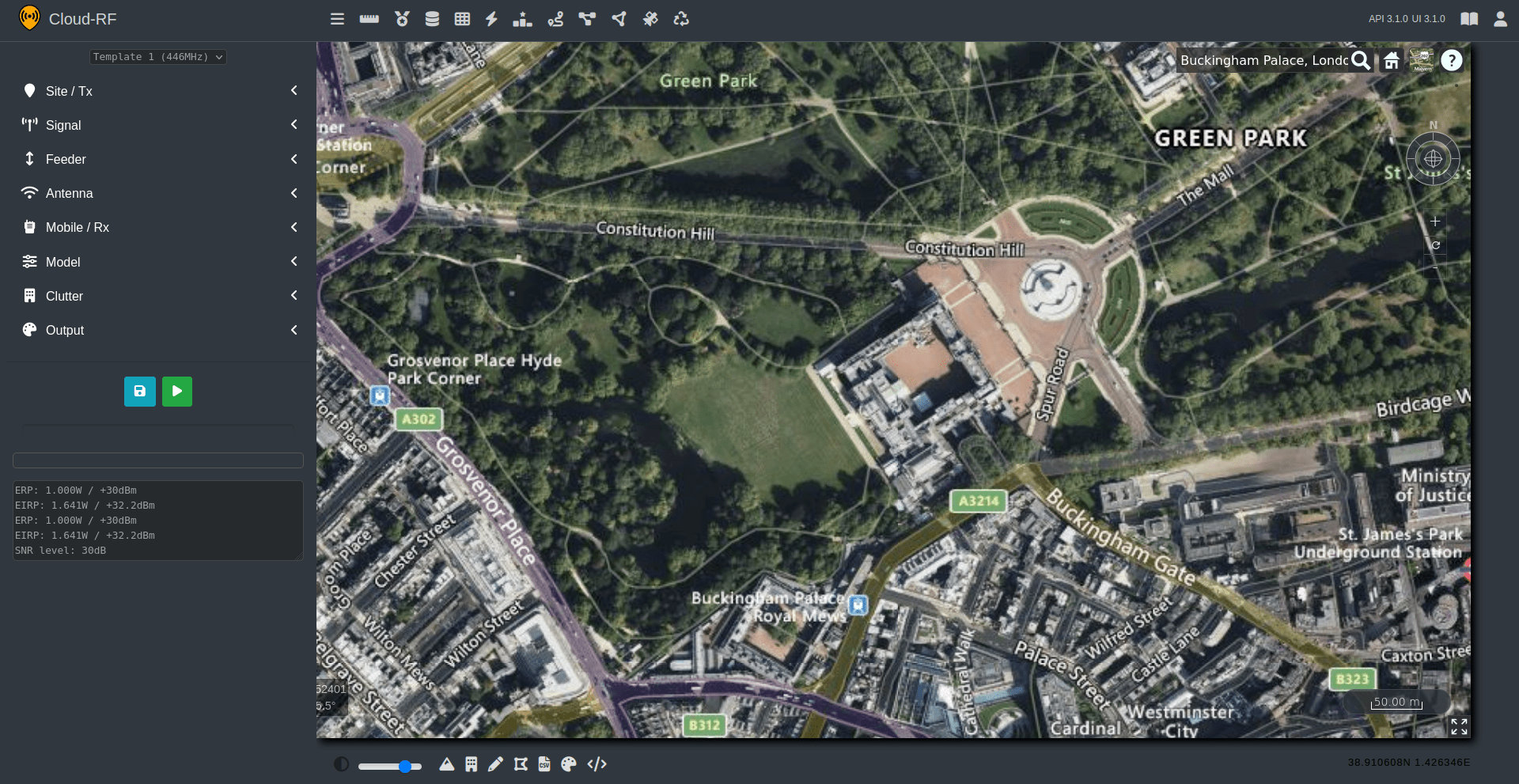
 View Home
View Home
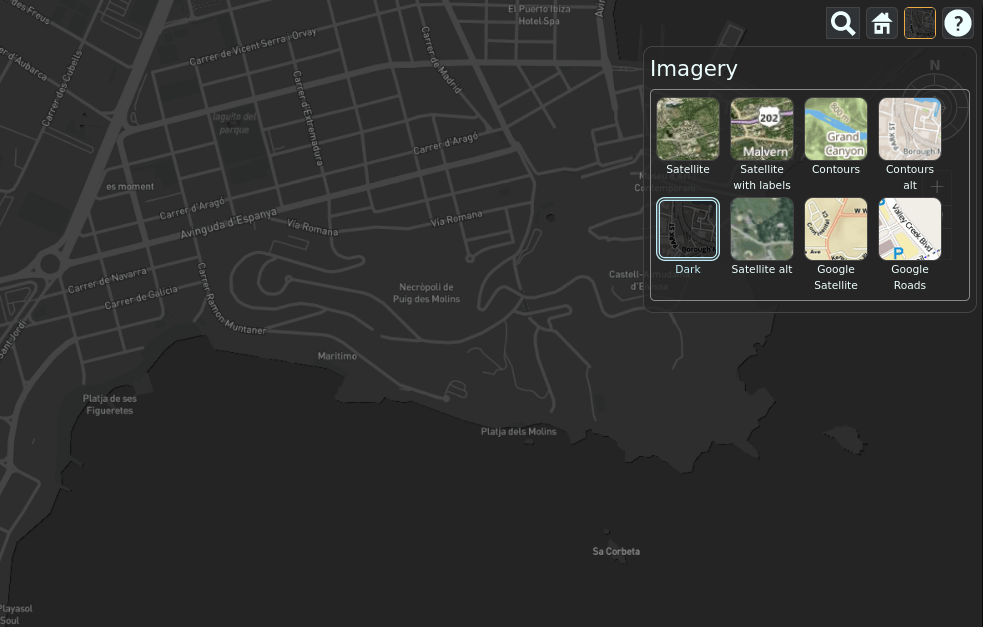
 Choosing Imagery
Choosing Imagery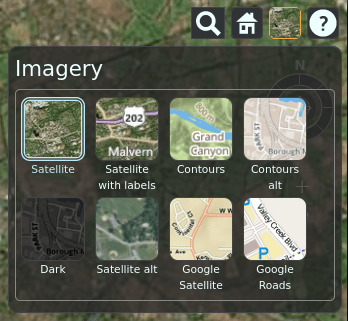
 icon located at the bottom-left of the interface.
icon located at the bottom-left of the interface. Navigation Instructions
Navigation Instructions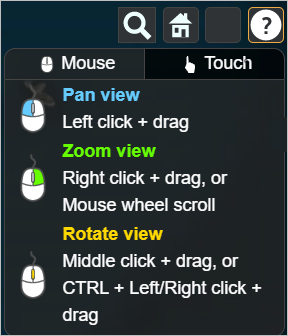
 tab.
tab. tab.
tab.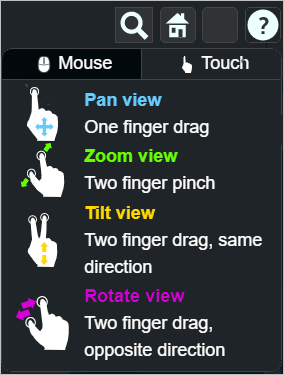
 Full Screen View
Full Screen View icon located at the bottom right of the 3D Interface.
icon located at the bottom right of the 3D Interface.
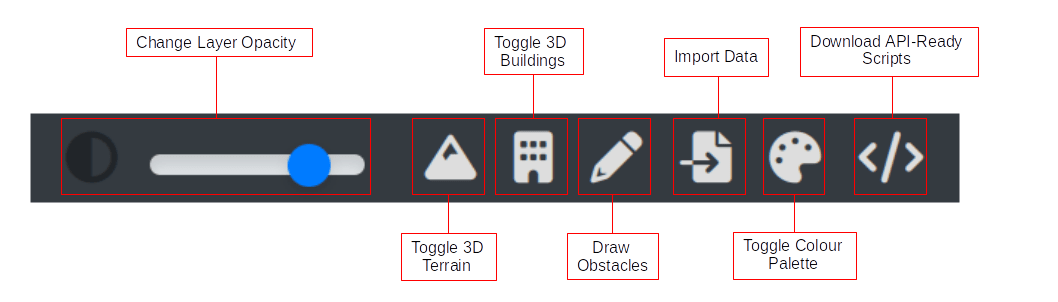

 icon indicates that the 3D Terrain has been enabled.
icon indicates that the 3D Terrain has been enabled.
 Toggle 3D Buildings
Toggle 3D Buildings icon indicates that the 3D Buildings have been enabled.
icon indicates that the 3D Buildings have been enabled.
 Draw Bounds
Draw Bounds Import Data
Import Data Toggle Colour Palette
Toggle Colour Palette Download API Ready Scripts
Download API Ready Scripts